How is the vehicle’s fuel exhaust system designed?
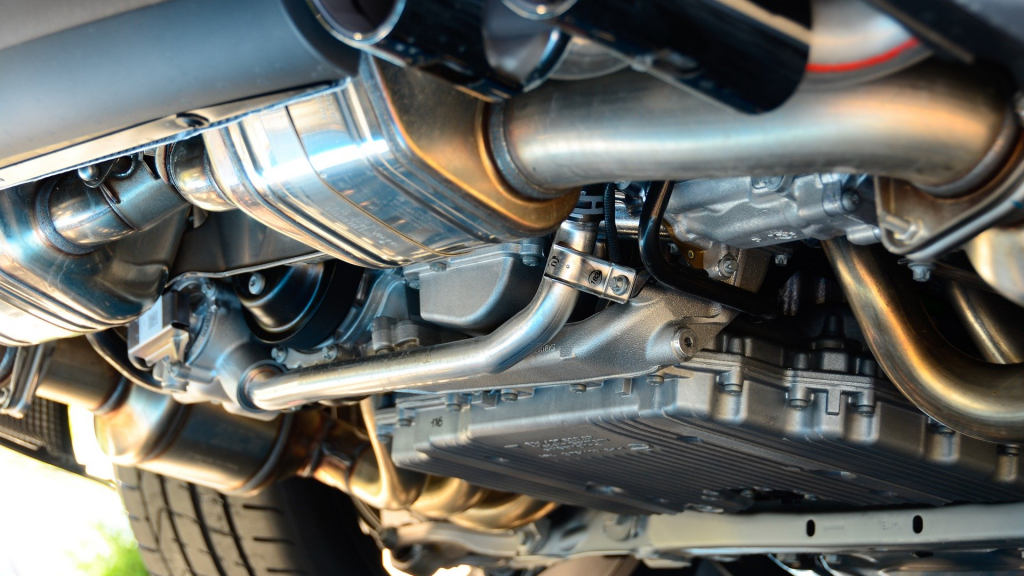
The fuel exhaust system is a key element of every vehicle, without which the car cannot function fully without its proper functioning. What are the exact elements in a fuel exhaust system?
The exhaust system consists of an exhaust manifold, a silencer and an exhaust pipe. In addition, the system includes a catalytic converter with a lambda sensor, and in the case of modern diesel engines, the exhaust system has a particulate filter otherwise known as a DPF filter.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD. The exhaust manifold is the first element of this system. It is mounted directly on the engine block and its function is to collect the exhaust gases from the engine cylinders. Later, the exhaust manifold “transports” the exhaust to the intended pipe. In the case of an engine with a diesel unit in the injection manifold, we find a turbocharger drive nozzle. In addition, a lambda probe may be installed in the exhaust manifold.
LAMBDA PROBE. The lambda probe is an electronic sensor responsible for measuring emissions. Its task is to compare the oxygen content of the exhaust with the oxygen content of the atmospheric air, so it is responsible for determining the composition of the fuel-air mixture. One part of the probe is inside the exhaust system and the other is outside. In the case of modern vehicles, we can accept two Lambda probes. The first is mounted in front of the catalyst and the second behind it. The first probe is responsible for the analysis of the composition of the mixture and has an influence on the determination of the composition of the fuel and air mixture, while the second performs the function of reporting and supervising the operation of the exhaust gas cleaning system.
CATALYST CONVERTER. Catalyst converter, is responsible for cleaning the exhaust from the car system. Exhaust gases can be cleaned due to the chemical reactions that take place in them, which reduce the release of harmful substances into the air. Good technical condition is the key to success in meeting emission standards. In addition, the poor condition of the catalyst converter contributes to the deterioration of engine performance.
SOUND SILENCER. Another part of the exhaust system is mufflers connected to the catalyst exhaust pipes. In most cases, two silencers are fitted in succession to the exhaust systems. Why? Because the first of these is an absorption muffler whose job is to suppress high sound frequencies. The second muffler is usually a chamber muffler responsible for attenuating low audio frequencies.
PARTICULATE FILTER (DPF). The particulate filter (DPF) is fitted to vehicles equipped with a diesel engine. The diesel particulate filter is a device to reduce emissions of environmentally harmful soot. It is installed immediately after the catalyst. The DPF filter has a built-in filtration system that allows the exhaust gas to flow by filtering it during that time, so that soot particles settle in the filter.
SILENCER. The muffler is an element located at the rear of the exhaust system. Its presence in the system is necessary for the exhaust gas treatment process to function properly in the system. In addition, the muffler has a direct effect in reducing the noise level.

The main tasks of the exhaust system are to properly discharge the exhaust gases from the engine so that the engine can function properly. In addition, the exhaust system significantly reduces the amount of harmful gases entering the atmosphere and reduces noise during engine operation.


